How Often Should Dental X-rays be Taken?
Posted by Dental Didactics CE on Aug 2nd 2022
What Information Do Dental X-rays Provide?
Initial dental examinations, and periodic recall examinations include dental x-rays to obtain critical diagnostic information. X-rays are taken to display general oral health information as well as track long-term changes in a patient's dentition and periodontal tissues. Some of the most important information provided by dental x-rays includes:
- Periodontal bone levels (related to periodontal disease and long-term tooth loss) which allow the dentist to diagnose current periodontal disease and compare bone levels over time to monitor bone loss
- Bony pathologies such as tumors and cysts
- Endodontic abscesses (root canal infections)
- Impacted wisdom teeth
- Sinus obstructions and cysts
- Caries (cavities)
- Missing teeth
- Jaw anatomy
- Orthodontic problems
- Cracked or broken fillings and crowns
- Implant health
- Root canal anatomy and treatment progress
- Sleep Apnea diagnosis
How Often Do Dental X-rays Need To Be Taken?
The periodic taking of dental x-rays should never be a standard interval (i.e. "every six months). The intervals between diagnostic dental x-rays should be determined by the individual patient's oral health, dental history, and current dental needs. Patients with a history of cavities and numerous dental restoration will need x-ray diagnosis on a more frequent basis, while patients with no history of cavities should have longer intervals between x-ray exams.
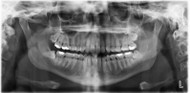
Academic and clinical authorities generally recommend a full mouth set of x-rays (or a panoramic x-ray) which show all the teeth, root ends and jaw every 3-7 years. The three year interval would be for adults with a history of cavities, numerous dental restorations, root canals, or periodontal disease. A seven year interval would be appropriate for patients with no clinical history of periodontal disease and minimal cavities and restorations.
Cavity check x-rays (bitewings) are recommended at intervals between 6 months and 2 years, depending on the patient's level of caries (cavity) activity. These allow the dentist to view "in between the teeth" where cavities start unseen by a visual examination. Bitewing x-rays are typically taken at 12-18 month intervals for the vast majority of patients. They allow dentists to diagnose cavities when they are in the early stages and before they have caused significant tooth damage which can lead to large fillings, crowns and root canals.
Many specific conditions demand individual x-rays at the time the pathology is treated:
- Wisdom tooth impactions
- Implant treatment planning or placement
- Root canal treatment
- Toothaches
- Orthodontic treatment
- Oral surgery (tooth extractions, cyst removal, bony surgery)
- Periodontal surgery
- Denture placement
Diagnostic x-rays are an essential part of dental diagnosis and treatment planning. Modern advancements in x-ray technology minimize radiation exposure and allow dentists to more accurately diagnose pathology and preserve oral health.
Dental Didactics CE offer many courses related to dental diagnosis and treatment at Dental Didactics CE Courses